
【Rでベイズ統計モデリング#19】ローカル線形トレンドモデル
記事の目的
状態空間モデルであるローカル線形トレンドモデルのベイズ推定を、RとStanを使用して実装していきます。データの作成から実装するので、コピペで再現することが可能です。
目次
0 前準備
0.1 今回のモデル

0.2 ワーキングディレクトリの設定
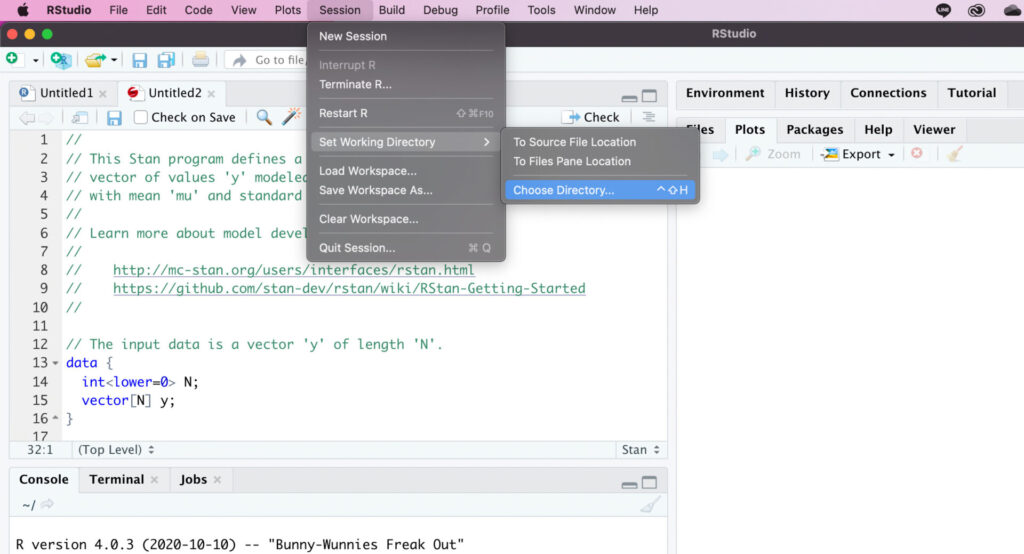
以下の画像のようにワーキングディレクトリを設定します。設定したディレクトリに、RファイルとStanファイルを保存します。
1 ライブラリ
# 1 ライブラリ library(dplyr) library(ggplot2) library(rstan) library(bayesplot) library(gridExtra) set.seed(2) rstan_options(auto_write=TRUE) options(mc.cores=parallel::detectCores())
2 データ
2.1 コード
# 2 データ
## 2.1 データの作成
日付 <- seq(as.POSIXct("2021/05/01"), as.POSIXct("2021/08/01"), "days")
売り上げ <- c()
mu <- c()
delta <- c()
mu[1] <- rnorm(1, 20, 1) %>% round(1)
delta[1] <- rnorm(1, 5, 1) %>% round(1)
T <- length(日付)
for(t in 2:T){
delta[t] <- rnorm(1, delta[t-1], 2)
mu[t] <- rnorm(1, mu[t-1]+delta[t-1], 5)
}
for(t in 1:T){
売り上げ[t] <- rnorm(1, mu[t], 3)
}
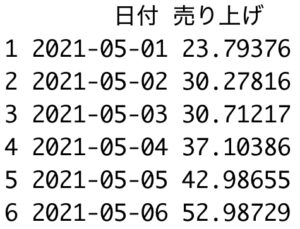
data <- data.frame(日付, 売り上げ)
data %>% head()
## 2.2 データの可視化
plot <- data %>%
ggplot(aes(x=日付)) +
theme_classic(base_family = "HiraKakuPro-W3") +
theme(text = element_text(size = 20))+
scale_x_datetime(date_labels = "%m/%d")
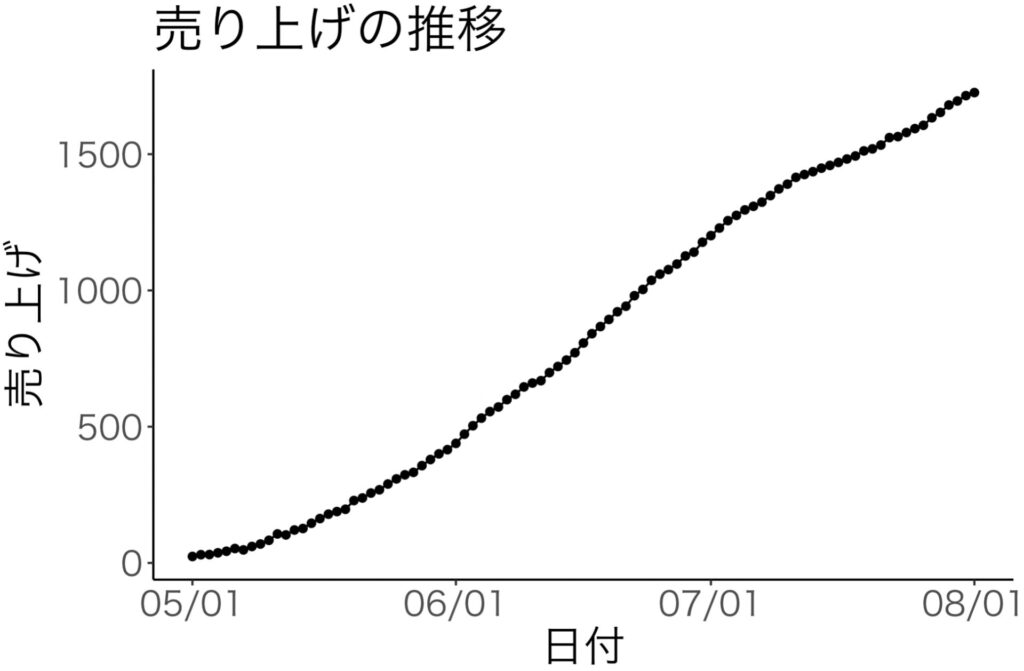
plot +
geom_point(aes(y=売り上げ))+
geom_line(aes(y=売り上げ)) +
labs(x="日付",y="売り上げ",title="売り上げの推移")
## 2.3 パラメータの可視化
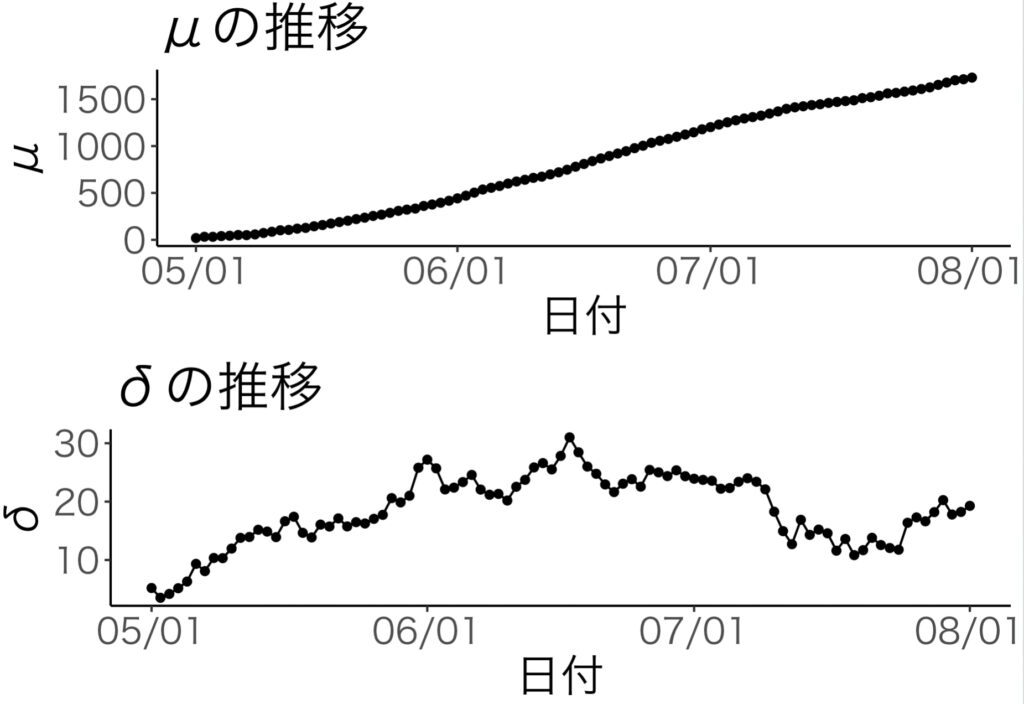
plot_mu_sim <- plot +
geom_point(aes(y=mu))+
geom_line(aes(y=mu)) +
labs(x="日付",y="μ",title="μの推移")
plot_delta_sim <- plot +
geom_point(aes(y=delta))+
geom_line(aes(y=delta)) +
labs(x="日付",y="δ",title="δの推移")
grid.arrange(plot_mu_sim, plot_delta_sim)
2.2 結果
| 18行目の結果 |
 |
| 27行目の結果 | 43行目の結果 |
 |
 |
3 Stanの利用
3.1 Stanファイル
data {
int T;
vector[T] y;
}
parameters {
vector[T] mu;
vector[T] delta;
real<lower=0> sigma_w;
real<lower=0> sigma_v;
real<lower=0> sigma_d;
}
model {
delta[2:T] ~ normal(delta[1:(T-1)], sigma_d);
mu[2:T] ~ normal(mu[1:(T-1)]+delta[1:(T-1)], sigma_w);
y ~ normal(mu, sigma_v);
}
generated quantities{
vector[T] y_pred;
for(t in 1:T){
y_pred[t] = normal_rng(mu[t], sigma_v);
}
}
3.2 Stanを利用するRのコード
# 3 stanの利用 data_list <- list( T = nrow(data), y = data$売り上げ ) mcmc_result <- stan( file="19ローカル線形トレンドモデル.stan", data=data_list, seed=1, iter = 2000, warmup = 200, chains = 3, thin=1 )
4 分析結果
4.1 コード
# 4 分析結果
## 4.1 推定結果
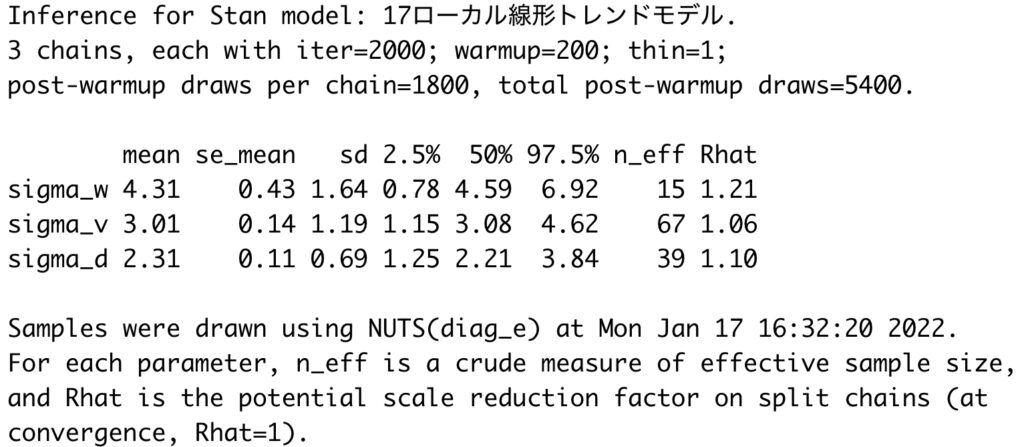
print(mcmc_result, pars=c("sigma_w", "sigma_v", "sigma_d"), probs = c(0.025, 0.5, 0.975))
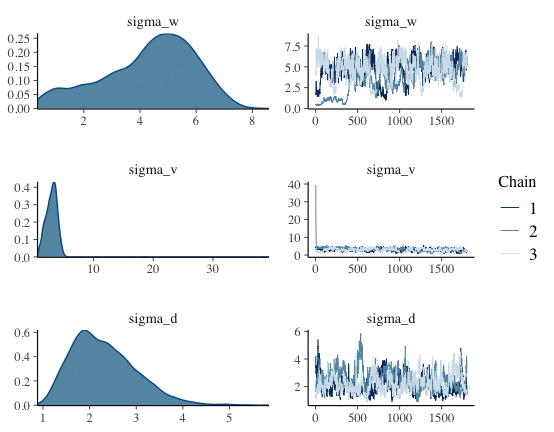
## 4.2 収束の確認
mcmc_sample <- rstan::extract(mcmc_result, permuted=FALSE)
mcmc_combo(mcmc_sample, pars=c("sigma_w","sigma_v","sigma_d"))
## 4.3パラメータの確認
mcmc_sample <- rstan::extract(mcmc_result)
func <- function(x){
return (quantile(x, c(0.025, 0.5, 0.975)))
}
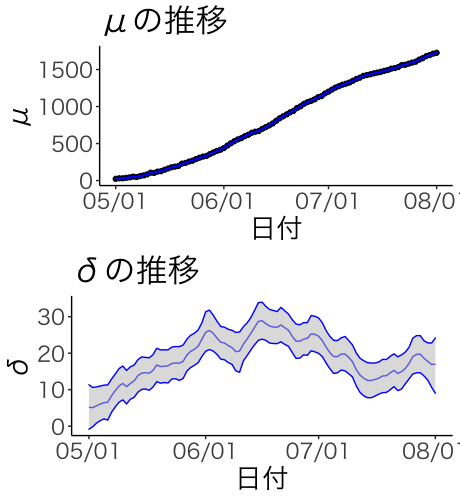
mu <- apply(mcmc_sample[["mu"]], 2, func)
plot_mu <- plot +
geom_point(aes(y=売り上げ))+
geom_line(aes(y=mu[2,]), col="blue") +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin=mu[1,],ymax=mu[3,]), alpha=0.5, fill="gray", col="blue") +
labs(x="日付",y="μ",title="μの推移")
delta <- apply(mcmc_sample[["delta"]], 2, func)
plot_delta <- plot +
geom_line(aes(y=delta[2,]), col="blue") +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin=delta[1,],ymax=delta[3,]), alpha=0.5, fill="gray", col="blue") +
labs(x="日付",y="δ",title="δの推移")
grid.arrange(plot_mu, plot_delta)
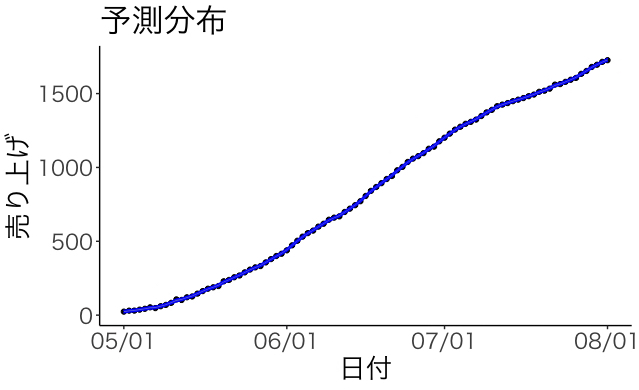
## 4.4 予測分布
y_pred <- apply(mcmc_sample[["y_pred"]], 2, func)
plot +
geom_point(aes(y=売り上げ))+
geom_line(aes(y=y_pred[2,]), col="blue") +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin=y_pred[1,],ymax=y_pred[3,]), alpha=0.5, fill="gray", col="blue") +
labs(x="日付",y="売り上げ",title="予測分布")
4.2 結果
| 3行目の結果 | 7行目の結果 |
 |
 |
| 28行目の結果 | 33行目の結果 |
 |
 |



